2020-09-24
Back to list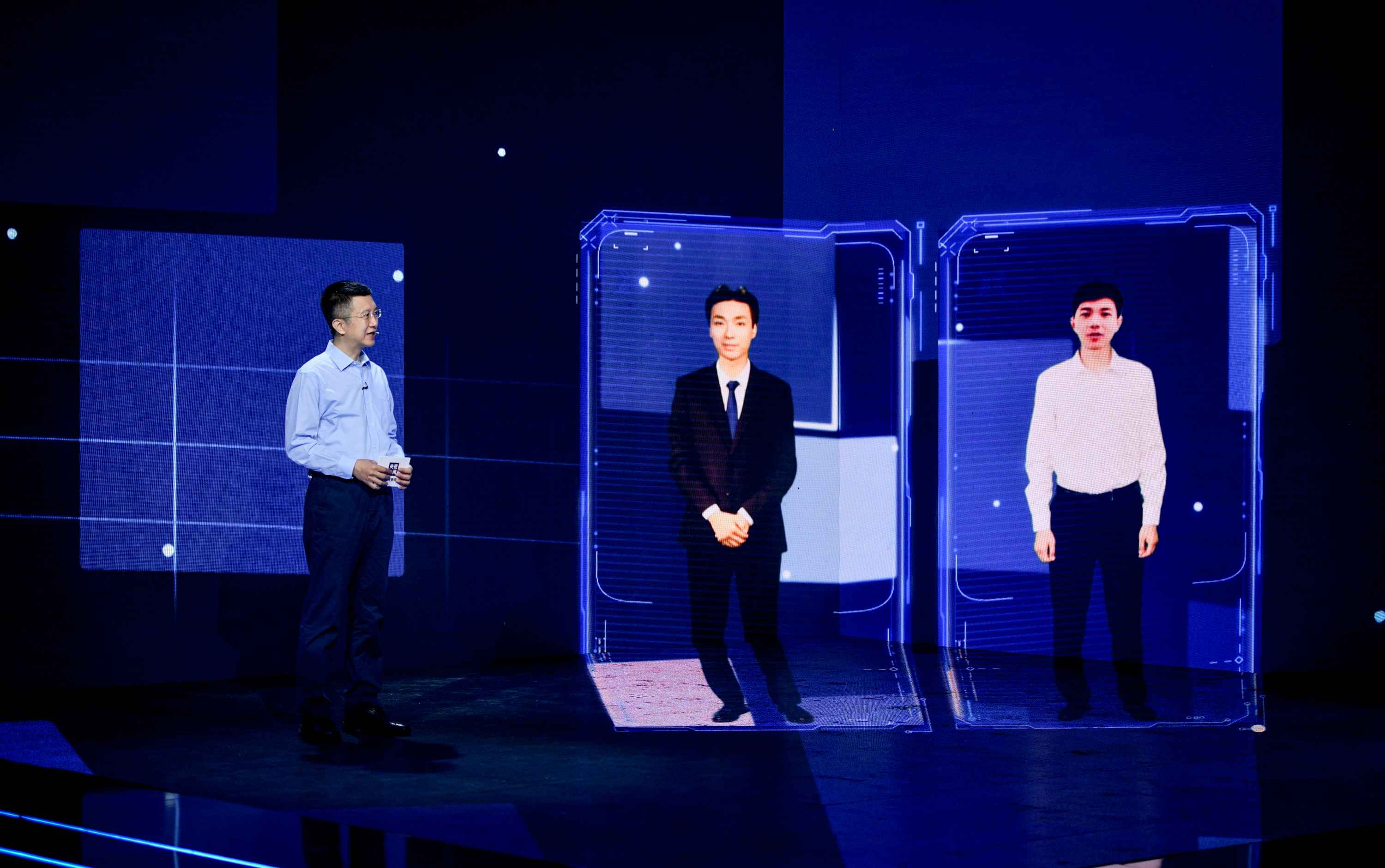
Last week, Baidu held Baidu World 2020, its biggest annual conference, where two virtual avatars were unveiled. The avatars resembled younger versions of Baidu Co-founder, Chairman, and CEO Robin Li and TV anchor Hui Kang in appearance, movements, and voice as they appeared on stage to talk with their human counterparts.
The virtual Li, who seamlessly and naturally chatted with the real Robin Li in Mandarin, is supported by a comprehensive suite of AI technologies from Baidu Brain, the company’s core AI technology engine and open AI platform, which has been upgraded to version 6.0. As of September 2020, Baidu Brain has developed more than 270 core AI capabilities and created over 310,000 models for developers, becoming a key driver of the intelligent transformation in a wide range of industries.
“Artificial intelligence is the core technology of the fourth-generation industrial revolution,” says Baidu CTO Haifeng Wang. “Baidu Brain can enable all industries to apply AI technology more efficiently, while accelerating the process of industrial intelligence.”
Join us for a quick look at Baidu Brain 6.0, including new updates in Baidu’s deep learning platform PaddlePaddle, AI processor Kunlun, core AI algorithms and a new quantum computing platform.
What is in Baidu Brain?
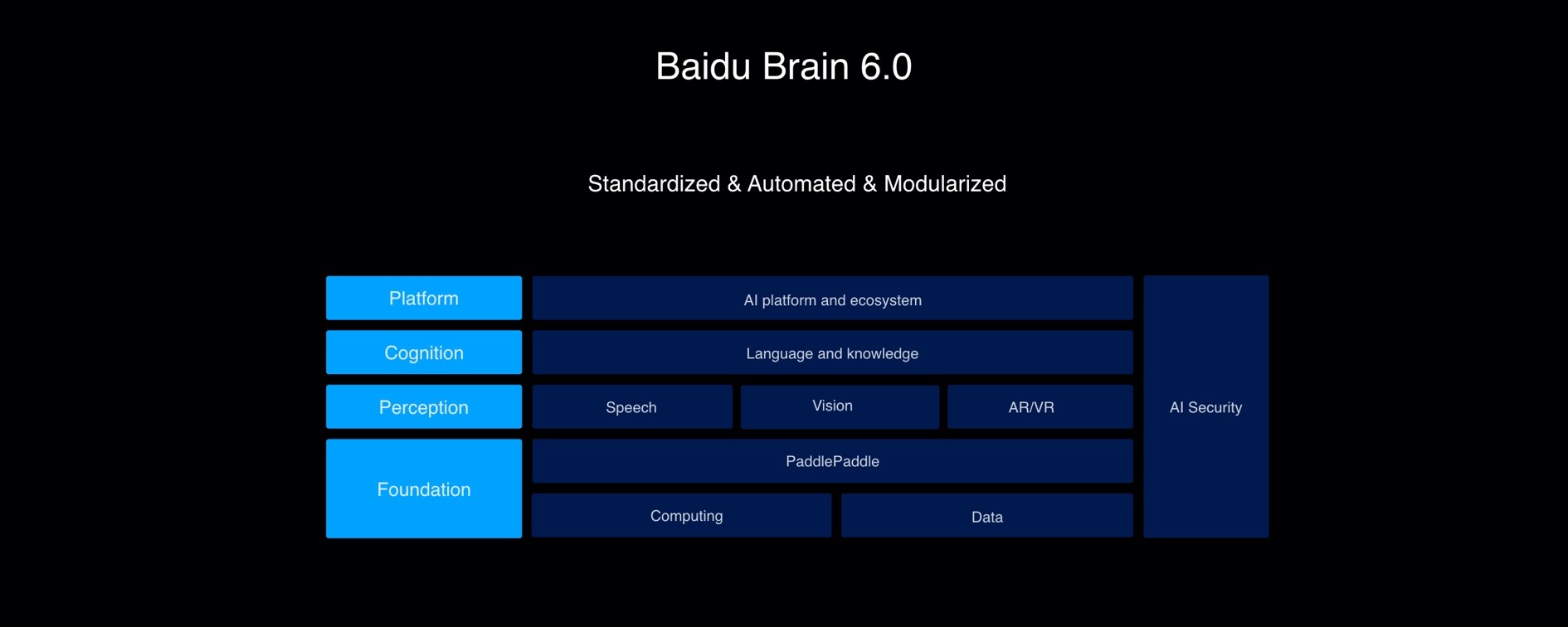
Since its debut in 2016, Baidu Brain has grown into a powerful technology driver that backs all Baidu businesses while opening up to third-party developers to accelerate a large-scale implementation of AI. Baidu Brain is segmented into four layers and one module:
A “foundation” layer consists of PaddlePaddle as software, Kunlun AI processors as hardware, and databases as the fuel;
A “perception” layer aggregates Baidu’s home-grown algorithm in voice technology, computer vision, and AR/VR;
A “cognition” layer acquires and integrates new information into Baidu’s large-scale knowledge graph;
A “platform” layer boosts an AI ecosystem;
An additional “AI security” module to guarantee Baidu Brain’s security, safety, and privacy.
PaddlePaddle supports dynamic and static computation graphs
As an easy-to-use deep learning platform, the newest release of PaddlePaddle features three major updates: more adaptive support for various hardware and processors; integrations of dynamic and static computation graphs; and a full upgrade of the API system.
The new PaddlePaddle supports 27 types of processors from 19 semiconductor manufacturers, including Intel, NVIDIA, and MediaTek. Such software-hardware optimization enables higher performance and accuracy of AI applications. For instance, the 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors triple the performance of Baidu’s natural language processing (NLP) model ERNIE on INT8 inference.
Another important change is the dynamic-to-static computation graph. One of the main differences between mainstream AI frameworks is the use of static or dynamic computational graphs. PaddlePaddle unifies the dynamic graph and static graph to strike a balance between flexibility and efficiency. Specifically, PaddlePaddle now provides support for the quantitative training and mixed precision training under a dynamic graph and implements syntax support in the dynamic-to-static conversion. As a result, mixed precision delivers 2.6 faster speed in training ResNet-50 model on V100 GPU versus FP32 with added support for mixed precision of dynamic graphs.
The platform also improves the API system by optimizing 155 APIs, adding 140 new APIs, and providing better high-level API functions that simplify common operations such as training, evaluation, and inference. For example, in the MNIST handwritten digit recognition task versus the imperative programming implementation mode, high-level APIs can reduce 80% of executable codes.
We are thrilled to see a growing developer community built around PaddlePaddle as third-party contributions have increased by 1,080%.
Kunlun 2 to be mass produced in 2021
In 2018, Baidu announced Kunlun, China’s first cloud-to-edge AI chip, built to accommodate high performance requirements for a wide variety of AI scenarios. The 14-nm chip offers 512 gigabytes per second (GBps) memory bandwidth and supplies up to 260 Tera operations per second (TOPS) at 150 watts. Nearly 20,000 Kunlun chips have been deployed to power Baidu’s applications including its search engine, with a 1.5-3 times performance boost over NVIDIA T4 GPU.
Our hardware team also provided a glimpse into the next-generation AI processor – Baidu Kunlun 2. The new chip uses 7 nm process technology and its top computational capability is over three times that of the previous generation. The mass production of the chip is expected to begin early next year.
Improved AI algorithms in voice, vision, and language
The standout capability of Baidu Brain 6.0 is the fusion of multimodal signals and knowledge to make progress in cognitive understanding, or we called “knowledge-enhanced multimodal deep semantic understanding”.
In voice technology, we proposed an end-to-end speech recognition modeling technology to integrate acoustic sensing and signal processing and designed multiple speech synthesis algorithms like personalized text-to-speech (TTS) and multi-speaker TTS. Over 15.5 billion calls have been made to Baidu’s speech API each day.
In computer vision, state-of-the-art efficiency is becoming a new trend to meet an increasing demand of edge-based computer vision applications. Baidu Brain 6.0 open sourced a series of lightweight vision models including the model that topped the “Real-time Image Classification Using Pixel 4 CPU” competition at CVPR 2020 and a 3.1M OCR model.
In language, Baidu’s NLP model ERNIE has learned approximately five billion knowledge pieces. Baidu Brain 6.0 also incorporates ERNIE’ variants in natural language generation (NLG), ERNIE-GEN, and visual semantic understanding, ERNIE-ViL.
Knowledge graphs are the building block for computers to develop a cognitive understanding of the world. Baidu Brain 6.0 has a large-scale knowledge graph with over five billion entities and 550 billion facts.
Quantum Leaf
This May, Baidu Quantum Computing Institute announced Paddle Quantum, a quantum machine learning development toolkit based on PaddlePaddle that can help scientists and developers quickly build and train quantum neural network models and provide advanced quantum computing applications.
At Baidu World 2020, the institute rolled out a new cloud-native quantum computing platform named Quantum Leaf. It is used for programming, simulating and executing quantum computers, aimed at providing the quantum programming environment for Quantum infrastructure as a Service (QaaS).
A key component in the Quantum Leaf architecture is QCompute, a Python-based open-source SDK. It provides a full-stack programming experience for advanced users via the features of hybrid quantum programming language and a high-performance simulator. Users can use the already-built objects and modules of quantum programming environment, pass parameters to build and execute the quantum circuits on the local simulator or the cloud simulator/hardware. QCompute provides services for creating and analyzing quantum circuits and calling quantum backend.
In addition to Paddle Quantum and Quantum Leaf, the institute also developed a cloud-based quantum pulse computing service named Quanlse, which aims to bridge the gap between quantum software and hardware. With Quanlse, Paddle Quantum, and Quantum Leaf, Baidu Quantum Platform moves further to its mission “Everyone Can Quantum”.